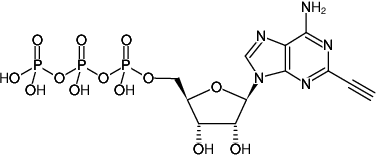
2-Ethynyl-ATP (2-EATP)
2-Ethynyl-adenosine-5’-triphosphate, Sodium salt
| Catálogo Nº | Apresentação | Preço (R$) | Comprar |
|---|---|---|---|
| CLK-NU-004S | 100 μl (10 mM) | Sob demanda | Adicionar ao Carrinho |
| CLK-NU-004L | 5 x 100 μl (10 mM) | Sob demanda | Adicionar ao Carrinho |
For general laboratory use.
Envio: shipped on gel packs
Condições de armazenamento: store at -20 °C
Short term exposure (up to 1 week cumulative) to ambient temperature possible.
Validade: 12 months after date of delivery
Fórmula molecular: C12H16N5O13P3
Peso molecular: 531.20 g/mol
Pureza: ≥ 90 % (HPLC), contains approx. 6 % 2-Ethynyl-ADP
Forma: solution in 100 mM Tris-HCl
Concentração: 10 mM - 11 mM
pH: 7.5 ±0.5
Propriedades espectroscópicas: λmax 265 nm, ε 10.6 L mmol-1 cm-1 (Tris-HCl pH 7.5)
Formulários:
in vitro polyadenylation of RNA[1]
Descrição:
2-Ethynyl-labeled adenosine triphosphate (2-EATP) is suitable for in vitro polyadenylation of RNA with recombinant poly(A) polymerase[1].
The resulting Alkyne-functionalized RNA can subsequently be processed via Cu(I)-catalyzed Azide-Alkyne click
chemistry (CUAAC) that offers the choice
to introduce a Biotin group for subsequent purification tasks (via Azides
of Biotin)to introduce fluorescent group for subsequent microscopic imaging (via
Azides of fluorescent dyes)to crosslink the RNA to azide-functionalized biomolecules e.g.proteins
Presolski et al.[2] and Hong et al.[3] provide a general protocol for Cu(I)-catalyzed click chemistry reactions that may be used as a starting point for the set up and optimization of individual assays.
Produtos relacionados:
- 5-Ethynyl-adenosine (5-EA), #CLK-N005
- Copper (II)-Sulphate (CuSO4), #CLK-MI004
- Tris(3-hydroxypropyltriazolylmethyl)amine (THPTA), #CLK-1010
- Sodium Ascorbate (Na-Ascorbate), #CLK-MI005
Referências selecionadas:
[1] Curanovic et al. (2013) Global profiling of stimulus-induced polyadenylation in cells using a poly (A) trap. Nat. Chem. Biol. 9:671.
[2] Presolski et al. (2011) Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry for Bioconjugation. Current Protocols in Chemical Biology 3:153.
[3] Hong et al. (2011) Analysis and Optimization of Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition for Bioconjugation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48:9879.
