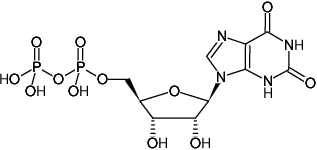
XDP
Xanthosine-5'-diphosphate, Sodium salt
| Catálogo Nº | Apresentação | Preço (R$) | Comprar |
|---|---|---|---|
| NU-601S | 100 μl (10 mM) | Sob demanda | Adicionar ao Carrinho |
| NU-601L | 5 x 100 μl (10 mM) | Sob demanda | Adicionar ao Carrinho |
For general laboratory use.
Envio: shipped on gel packs
Condições de armazenamento: store at -20 °C
Short term exposure (up to 1 week cumulative) to ambient temperature possible.
Validade: 12 months after date of delivery
Fórmula molecular: C10H14N4O12P2 (free acid)
Peso molecular: 444.18 g/mol (free acid)
CAS#: 29042-61-3
Pureza: ≥ 95 % (HPLC)
Forma: solution in water
Concentração: 10 mM - 11 mM
pH: 7.5 ±0.5
Propriedades espectroscópicas: λmax 276 nm, ε 9.6 L mmol-1 cm-1 (Tris-HCl pH 7.5)
Referências selecionadas:
Chang et al. (2005) Nitric Oxide-dependent Allosteric Inhibitory Role of a Second Nucleotide Binding Site in Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 280 (12):11513.
Legate et al. (2000) Nucleotide-dependent binding of the GTPase domain of the signal recognition particle receptor betasubunit to the alpha-subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (35):27439.
Brown et al. (1999) Crystal structure of the bifunctional N-acetylglucosamine 1-phosphate uridyltransferase from Escherichia coli: a paradigm for the related pyrophosphorylase superfamily. EMBO J. 18 (15):4096.
Yu et al. (1998) Interaction of the xanthine nucleotide binding Go alpha mutant with G protein-coupled receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 273 (46):30183.
Barbieri et al. (1998) Evidence for a symmetrical requirement for Rab5-GTP in in vitro endosome-endosome fusion. J. Biol. Chem. 273 (40):25850.
Yu et al. (1997) Characterization of a Go alpha mutant that binds xanthine nucleotides. J. Biol. Chem. 272 (29):18015.
Schmidt et al. (1996) Biochemical and biological consequences of changing the specificity of p21 (ras) from guanosine to xanthosine nucleotides. Oncogene 12 (1):87.
Weijland et al. (1994) Elongation-factor Tu DL38n, a mutant with modified substrate-specificity, as a tool to study energyconsumption in protein-biosynthesis. Biochemistry-US 33 (35):10711.
