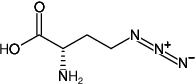
4-Azido-L-homoalanine HCl (L-AHA)
(S)-2-Amino-4-azidobutanoic acid hydrochloride
| Catálogo Nº | Apresentação | Preço (R$) | Comprar |
|---|---|---|---|
| CLK-AA005-10 | 10 mg | Sob demanda | Adicionar ao Carrinho |
| CLK-AA005-100 | 100 mg | Sob demanda | Adicionar ao Carrinho |
| CLK-AA005-500 | 500 mg | Sob demanda | Adicionar ao Carrinho |
For general laboratory use.
Envio: shipped on gel packs
Condições de armazenamento: store at 4 °C
store dry
Validade: 12 months after date of delivery
Fórmula molecular: C4H8N4O2
Peso molecular: 144.13 g/mol
CAS#: 942518-29-8
Pureza: mass identification conforms (ESI-MS)
Forma: powder
Formulários:
Proteins synthesis monitoring[1,2,3]
Descrição:
4-Azido-L-homoalanine (L-AHA) provides a non-radioactive alternative to analyze the global protein synthesis in cell culture. It is cell-permeable and randomly incorporated instead of methionine during translation[1,2,3]. The resulting azide-labeled full-length proteins can subsequently be detected via Cu(I)-catalyzed or Cu(I)-free click chemistry that offers the choice to introduce a Biotin group (via Azides of Biotin or DBCO-containing Biotin, respectively) for subsequent purification tasks or a fluorescent group (via Azides of fluorescent dyes or DBCO-containing fluorescent dyes, respectively) for subsequent microscopic imaging.
Presolski et al.[4] and Hong et al.[5] provide a general protocol for Cu(I)-catalyzed click chemistry reactions that may be used as a starting point for the set up and optimization of individual assays.
Produtos relacionados:
- Copper (II)-Sulphate (CuSO4), #CLK-MI004
- Tris(3-hydroxypropyltriazolylmethyl)amine (THPTA), #CLK-1010
- Sodium Ascorbate (Na-Ascorbate), #CLK-MI005
Referências selecionadas:
[1] Dieck et al. (2012) Metabolic Labeling with Noncanonical Amino Acids and Visualisation by Chemoselective Fluorescent Tagging. Current Protocols in Cell Biology 7:7.11.1.
[2] Kiick et al. (2002) Incorporation of azides into recombinant proteins for chemoselective modification by the Staudinger ligation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 (1):19.
[3] Dieterich et al. (2010) In situ visualization and dynamics of newly synthesized proteins in rat hippocampal neurons. Nature Neuroscience 13 (7): 897.
[4] Presolski et al. (2011) Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry for Bioconjugation. Current Protocols in Chemical Biology 3:153.
[5] Hong et al. (2011) Analysis and Optimization of Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition for Bioconjugation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48:9879.
