JBS dNTP-Mutagenesis Kit
Random Mutagenesis by dNTP Analogs
| Catálogo Nº | Apresentação | Preço (R$) | Comprar / Observação |
|---|---|---|---|
| PP-101 | 15 reactions | Sob demanda | Adicionar ao Carrinho |
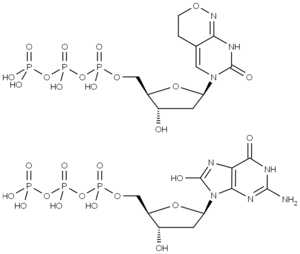
Fig. 1: Estruturas de dPTP e 8-Oxo-dGTP
![Fig 2 Grau de mutagênese em função do número de ciclos de PCR [Zaccolo et al]](/images/0c2100e9cd/PP-101_Bild_2.png)
Fig. 2: Grau de mutagênese em função do número de ciclos de PCR [Zaccolo et al.]
For general laboratory use.
Envio: Shipped on gel packs
Condições de armazenamento: Store at -20 °C
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles, aliquoting of the modified nucleotides prior to use is strongly recommended
Validade: 12 months
Descrição:
Random Mutagenesis by dNTP Analogs
This method is based on the incorporation of mutagenic dNTP analogs, such as 8-oxo-dGTP and dPTP, into an amplified DNA fragment by PCR. The mutagenic dNTPs are eliminated by a second PCR step in the presence of the four natural dNTPs only, resulting in a rate of mutagenesis of up to 20%.
Contente:
Taq Polymerase (red cap)
5 units/μl, 40 μl
Mutagenesis Buffer (green cap)
10x concentration, 200 μl
dNTP Mix (white cap)
10 mM each dNTP (dATP, dCTP, dGTP,dTTP), 100 μl
dPTP (yellow cap)
10 mM, 40 μl
8-oxo-dGTP (blue cap)
10 mM, 40 μl
PCR-grade Water (white cap)
2x 1 ml
Random mutagenesis by dNTP analogs
8-oxo-dGTP as well as dPTP are mutagenic dNTP analogs which are incorporated into DNA by PCR using Taq polymerase [Zaccolo et al., Zang et al.].
8-Oxo-dGTP is incorporated opposite template adenine yielding two transition mutations: A→C:T→G. A total rate of mutagenesis of approx. 2% (Fig. 2) has been reported, with A→C:T→G occurring at a ratio of approx. 1:1.5.
The dNTP analog dPTP has been reported to be approx. 10-fold more mutagenic than 8-oxo-dGTP (Fig. 2). The mutations induced by dPTP occur at a ratio of approximately 5:4:1:1 (A→G:T→C:G→A:C→T), with a total rate of mutagenesis of up to 19%.
Random mutagenesis induced by 8-Oxo-dGTP and/or dPTP is carried out in a two-step PCR process. First, the target DNA fragment is amplified in the presence of the four natural dNTPs plus the mutagenic analogs dPTP and/or 8-Oxo-dGTP. The rate of mutagenesis can be easily controlled by the number of PCR-cycles (Fig. 2).
The product of the first PCR is then subjected to a second PCR in the absence of mutagenic analogs. This step eliminates the non-natural analogs from the target DNA before cloning and transformation.
Recommended assay preparation
- For a 50 μl reaction, take 5 μl of 10x Mutagenesis Buffer in a sterile vial
- Add up to 25 fmol template DNA and 0.2-1 μM of appropriate primers
- Add 2.5 μl of dNTP Mix
- Add 2.5 μl of each mutagenic analog
- Add 1 μl (5 u) of Taq Polymerase
- Add PCR-grade Water to a final volume of 50 μl
Recommended thermocycling conditions
| Denaturation | 92°C | 1 min |
| Annealing 1) | 55-60°C | 1.5 min |
| Extension | 72°C | 5 min |
Number of cycles: 5-30 (refer to Fig. 2)
The rate of mutagenesis mainly depends on the number of cycles (Fig. 2) and can additionally be fine-tuned by the amount of mutagenic dNTP’s [Zaccolo et al.].
1) The annealing temperature depends on the melting temperature of the primers and should be adapted to the used primer set.
Final PCR
For elimination of the mutagenic dNTPs, use an aliquot of 1 μl of the first PCR reaction as template in a second PCR. Take 10x Mutagenesis Buffer and add template, primers, dNTP Mix and Taq Polymerase in same concentrations as above. Fill up with PCR-grade Water to 50 μl.
Use the same thermocycling conditions but 20-30 cycles.
Referências selecionadas:
Zang et al. (2006) Efficient and high fidelity incorporation of dCTP opposite 7,8-dihydro-8-oxodeoxyguanosine by sulfolobus solfatarius DNA polymerase Dpo4. Journal of Biological Chemistry 281:2358.
Zaccolo et al. (1999) The effect of high-frequency random mutagenesis on in vitro protein evolution: a study on TEM-1 beta-lactamase. J. Mol. Biol. 285 (2):775.
Crameri et al. (1998) DNA shuffling of a family of genes from diverse species accelerates directed evolution. Nature 391:288.
Zaccolo et al. (1996) An approach to random mutagenesis of DNA using mixtures of triphosphate derivatives of nucleoside analogues. J. Mol. Biol. 255:589.
Stemmer (1994) Rapid evolution of a protein in vitro by DNA shuffling. Nature 370:389.
Cadwell et al. (1992) Randomization of genes by PCR mutagenesis. PCR Meth. Appl. 2:28.
